Pixel Value Remapping for a 16 Bit Version of AIR
- When the AIR package is compiled, it is compiled either as an
8 bit or as a 16 bit version. The
information on this page describes the pixel value remapping
behavior of AIR when it is compiled in 16 bit format. All 16 bit
versions of AIR represent pixel values internally using numbers
ranging from zero to 65535. Your image generation and display
software may require that data be represented differently, so the
AIR package allows pixel values to be systematically remapped when
loading data from disk or
saving data to disk.
Loading data from disk into a 16 bit
version of AIR
- When loading type 0 data (8
bit data) from disk, a 16 bit version of the AIR package will:

-
- When loading16 bit type 1
data from disk, a 16 bit version of the AIR package will:

-
- When loading 16 bit type 2
data from disk, a 16 bit version of the AIR package will:
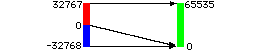
-
- set negative values to zero
- multiply by 2
- When loading 16 bit type 3
data from disk, a 16 bit version of the AIR package will:

-
Saving data from a 16 bit version of
AIR
When a 16 bit version of the AIR package is compiled, a default 16
bit storage data type is selected (the storage data type is specified
in the config.h file). All data (except for binary files)
generated by that compiled version of the AIR package will be saved
to disk using the data type that was specified at compilation.
Consequently, the output data type (which is fixed for any given
compilation) will not necessarily match the input data type (which
can be any data type).
- If a 16 bit version of AIR was compiled to generate external
type 1 data
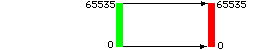
-
- no adjustment is made when writing data to disk
- If a 16 bit version of AIR was compiled to generate external
type 2 data
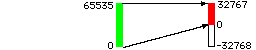
-
- values are divided by 2 before writing them to disk
- If a 16 bit version of AIR was compiled to generate external
type 3 data
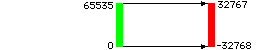
-
- 32768 is subtracted from values before writing them to disk
 Modified: February 12, 2002
Modified: February 12, 2002
© 1995-2002 Roger P. Woods,
M.D.(rwoods@ucla.edu)






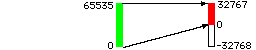
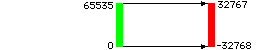
 Modified: February 12, 2002
Modified: February 12, 2002